
In an era of digital transformation, the healthcare industry is increasingly dependent on technology for storing, managing, and sharing patient data. Electronic Health Records (EHRs), telemedicine, wearable devices, and cloud-based health platforms have revolutionized patient care, but they also introduce significant healthcare data security challenges. Ensuring data privacy and protecting sensitive information against cyber threats is now more critical than ever.
This blog post delves into the cybersecurity risks in healthcare, the importance of data security in healthcare, and outlines best practices for securing patient data, helping stakeholders build robust and secure digital healthcare systems.
Understanding Healthcare Data Security Challenges
Healthcare data security challenges stem from the sheer volume, sensitivity, and value of patient information. Healthcare data includes personal identification details, medical histories, insurance data, billing information, and even genetic profiles. This makes the sector a prime target for cybercriminals.
Here are some major challenges:
- Legacy Systems: Many hospitals still use outdated software and infrastructure that lack modern security features. These legacy systems are difficult to patch and integrate with newer tools, leaving significant gaps in security defenses.
- Lack of Awareness: Human error remains a top cause of breaches. When staff aren’t trained in cybersecurity best practices—like recognizing phishing emails or securing passwords—they unintentionally become a vulnerability.
- Increased Attack Surface: With the rise of telehealth, mobile apps, wearable trackers, and connected devices, the number of endpoints has expanded drastically. Each connected device becomes a potential entry point for cyberattacks if not properly secured.
- Third-party Vendors: Healthcare providers often partner with external vendors for billing, diagnostics, or IT services. If these vendors don’t follow strict security protocols, they become weak links in the chain, exposing patient data to breaches.
- Compliance Complexity: Healthcare providers must navigate multiple regulations like HIPAA (U.S.), GDPR (EU), or India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act. Compliance is not only time-consuming but also requires consistent monitoring, updating, and documentation.
Also read- Technology in Medical Field | Modern Healthcare 2025
Healthcare Data Security Challenges: Cybersecurity Risks in Healthcare
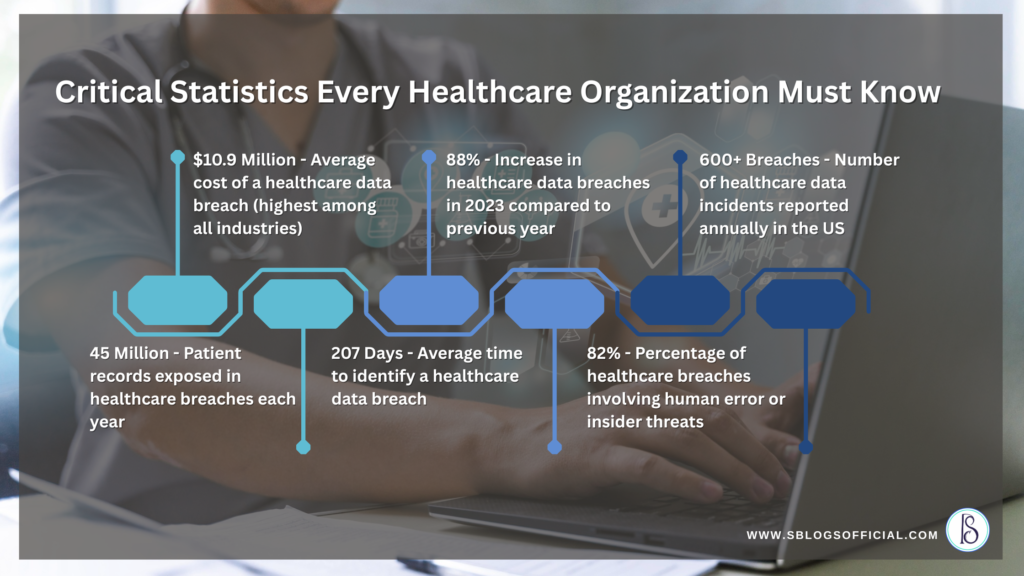
The cybersecurity risks in healthcare are vast and evolving. According to a report by IBM, the average cost of a healthcare data breach in 2023 was over $10 million, higher than in any other sector.
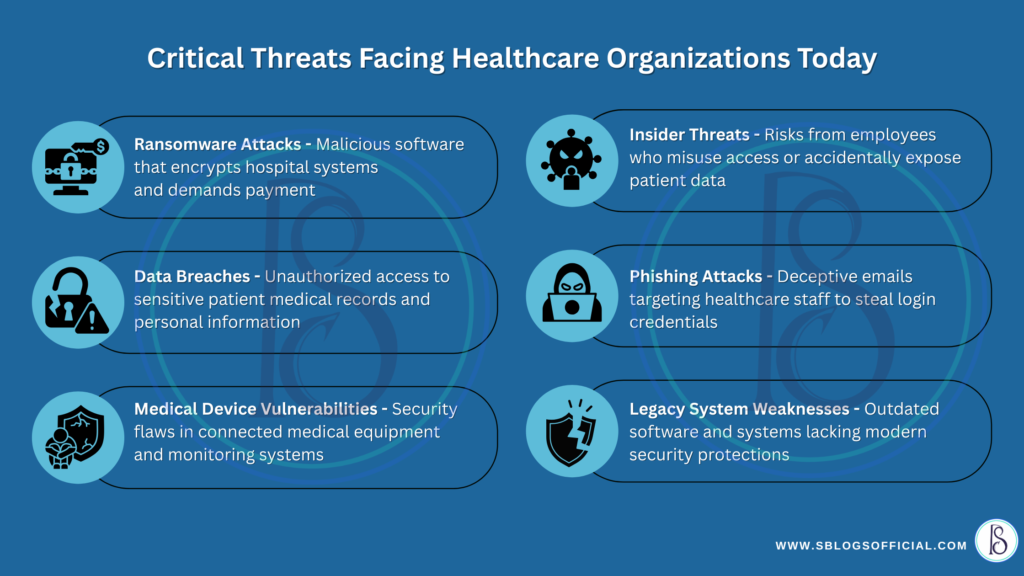
Key threats include:
1. Ransomware Attacks
Cybercriminals encrypt patient data and demand a ransom to unlock it. In some cases, hospitals have had to shut down services temporarily, affecting patient care and operational continuity.
2. Phishing Campaigns
Hackers send fraudulent emails to healthcare staff, tricking them into clicking malicious links or providing login credentials. A single mistake can compromise entire systems.
3. Insider Threats
Not all threats come from outside. Employees—whether negligent or malicious—can intentionally leak or accidentally expose sensitive data.
4. DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service attacks flood healthcare servers with traffic, crashing systems and cutting off access to critical patient data.
5. Data Theft for Profit
Health records are extremely valuable on the dark web due to the amount of personal, financial, and insurance data they contain. Unlike credit card info, which can be canceled, health data is permanent.
Importance of Data Security in Healthcare
The importance of data security in healthcare cannot be overstated. Breaches not only result in financial losses but also erode patient trust, disrupt care delivery, and can even have legal consequences.
Data security ensures:
1. Patient Trust
Patients are more likely to share complete and honest information if they trust that their data is safe. Without this trust, care quality suffers.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Failing to comply with data protection laws can result in heavy fines, legal action, and reputational damage. Robust security systems help meet these requirements proactively.
3. Continuity of Care
When systems are disrupted by breaches or malware, patient services can grind to a halt. Strong security ensures uninterrupted care, especially in emergencies.
4. Data Integrity
Clinicians rely on accurate data for diagnosis, treatment, and research. Protecting records from tampering or corruption is vital to clinical accuracy.
Also read- AI in Medical Devices | Improving Patient Care | 2024 Insights
Best Practices for Securing Patient Data in Order to Overcome Healthcare Data Security Challenges
Implementing the best practices for securing patient data to manage healthcare data security challenges requires a multi-layered approach involving people, processes, and technology. Here’s how healthcare organizations can strengthen their data protection posture:
1. Data Encryption
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit makes it unreadable to unauthorized users, even if it’s stolen. Strong encryption algorithms are the foundation of secure data handling.
2. Access Controls
Role-based access ensures staff only view the information necessary for their duties. This limits exposure and tracks user activity.
3. Regular Risk Assessments
Conducting security audits and risk assessments helps identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. This also ensures compliance with evolving regulations.
4. Employee Training
All staff medical and administrative must be educated on phishing, password safety, and proper data handling. Cybersecurity awareness is everyone’s responsibility.
5. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond usernames and passwords. Even if a password is compromised, access remains blocked without a second authentication method.
6. Patch Management
Timely updates to software and operating systems close known security gaps. Automating patch deployment ensures nothing gets missed.
7. Secure Backup Systems
Regularly back up critical data and store it securely offline. In the event of a ransomware attack, backups allow systems to be restored without paying a ransom.
8. Vendor Management
Evaluate and audit the security practices of third-party vendors. Use contracts to ensure they follow the same data protection standards as the healthcare organization.
9. Incident Response Plan
Prepare a documented and tested response plan outlining how to detect, respond to, and recover from data breaches. This reduces downtime and minimises damage.
Also Read- Game-Changing Medical Breakthroughs 2024
Best Practices for Securing Patient Data
| Security Practice | Implementation Method | Key Benefits | Risk Level if Ignored |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Require password + SMS/app code + biometric verification | Blocks 99.9% of automated attacks | CRITICAL – Single point of failure |
| Data Encryption | Use AES-256 encryption for data at rest and in transit | Makes stolen data unreadable | HIGH – Data breaches expose patient info |
| Access Controls | Role-based permissions with minimum necessary access | Limits internal data exposure | HIGH – Insider threats increase |
| Regular Security Audits | Quarterly penetration testing and vulnerability scans | Identifies weaknesses before hackers | MEDIUM – Unknown vulnerabilities persist |
| Staff Training | Monthly cybersecurity awareness sessions | Prevents 95% of phishing attacks | HIGH – Human error causes 80% of breaches |
| Backup & Recovery | Daily automated backups with the 3-2-1 rule | Ensures data availability during attacks | CRITICAL – Ransomware can destroy operations |
| Network Segmentation | Isolate patient data systems from the general network | Contains breaches and limits damage | MEDIUM – Lateral movement by attackers |
| Incident Response Plan | Documented procedures for breach response | Reduces breach impact by 50% | HIGH – Delayed response increases damage |
| Device Management | Endpoint protection and remote wipe capabilities | Secures mobile devices and laptops | MEDIUM – Lost devices expose data |
| Vendor Security Assessment | Annual security reviews of third-party partners | Prevents supply chain attacks | MEDIUM – Third-party breaches affect patients |
Healthcare Data Security: A Shared Responsibility
Securing healthcare data is not the responsibility of IT departments alone. It requires collaboration among healthcare providers, administrators, policymakers, and patients. A culture of cybersecurity awareness, continuous monitoring, and proactive defense can go a long way in mitigating risks.
The future of digital healthcare relies on a secure and privacy-focused infrastructure. Addressing healthcare data security challenges now will enable better patient outcomes, improved operational efficiency, and a safer digital ecosystem.
Also Read- Virtual Nurse Assistant | The Future of 24/7 AI Healthcare Support
Final Thoughts
Digital innovation in healthcare offers immense potential to tackle healthcare data security challenges, but with it comes equally significant risks. From legacy systems to phishing and ransomware, the challenges are real and growing. However, with the right tools, training, and mindset, these threats can be managed.
By embracing best practices and fostering a culture of cybersecurity, healthcare organizations can protect patient data, maintain operational continuity, and safeguard the trust that forms the heart of patient care.
In the future of digital health, security isn’t optional—it’s foundational. Let’s ensure that healthcare continues to evolve without compromising the privacy and safety of those it serves.
References
- Digital Guardian. (n.d.). Healthcare Data Security: Challenges & Strategies. Retrieved from Healthcare Data Security: Challenges & Solutions | Digital Guardian
- IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023
- HIPAA Journal. (n.d.). Healthcare Data Breaches: Causes and Solutions
- HealthIT.gov. (n.d.). Privacy and Security of Electronic Health Information
