
Have you ever wondered why two people with identical genes can have completely different health outcomes? The answer lies in the fascinating world of epigenetics, where genetic methylation testing is revolutionizing our understanding of how our bodies actually function at the cellular level. This cutting-edge diagnostic tool reveals the hidden switches that turn your genes on and off, providing unprecedented insights into your metabolism, detoxification pathways, and disease susceptibility. Unlike traditional genetic testing, which only shows what genes you have, genetic methylation testing uncovers how the expression of genes occurs in your body right now. By understanding your unique methylation patterns, you can unlock personalised strategies for optimising your health, preventing disease, and addressing the root causes of chronic conditions that have puzzled both patients and practitioners for years.
What If Your Genes Could Talk?
Imagine having a blueprint of your body’s health responses, your genes. In simple terms, DNA acts like a Recipe Book for your body. Meanwhile, genes are the Recipes inside your DNA that instruct your body on how to make certain proteins. Essentially, they both act as an instruction Manual, which instructs your body on how to function.
DNA is shaped like a double Helix, which appears as a twisted ladder. The backbone of this ladder, or its spine, is composed of sugar and phosphate. The steps of the ladder are made up of 4 chemical bases, which are A, T, G, and C, where the information is stored.
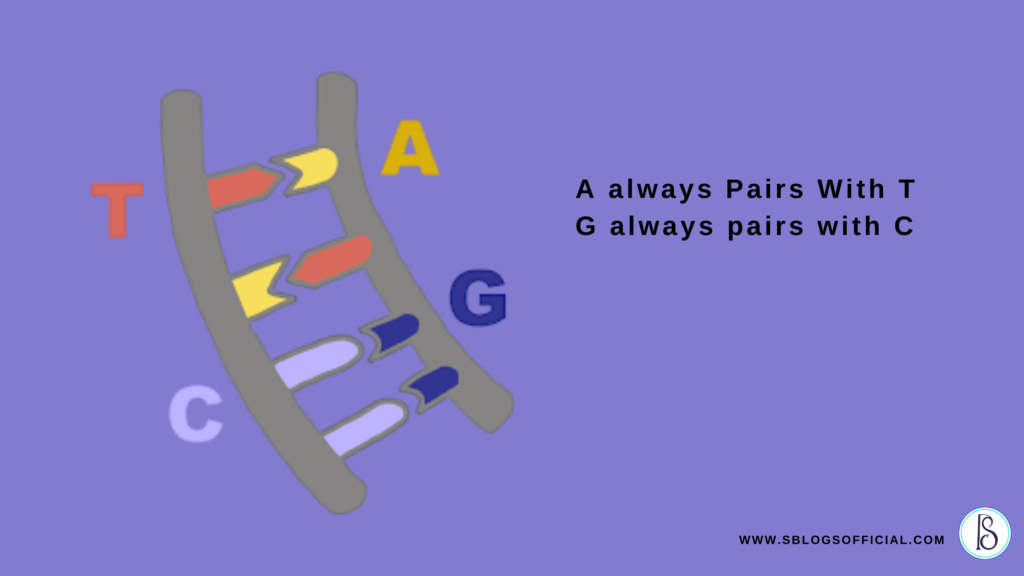
For instance, in DNA,
- A always Pairs With T
- G always pairs with C
Advancements in modern genetic testing have enabled us to gain a more comprehensive and molecular-level understanding of our health, including DNA methylation. This DNA methylation plays one of the most crucial biological functions, which has a direct impact on our health and vitality.
What Is Methylation and Why Is It So Important?
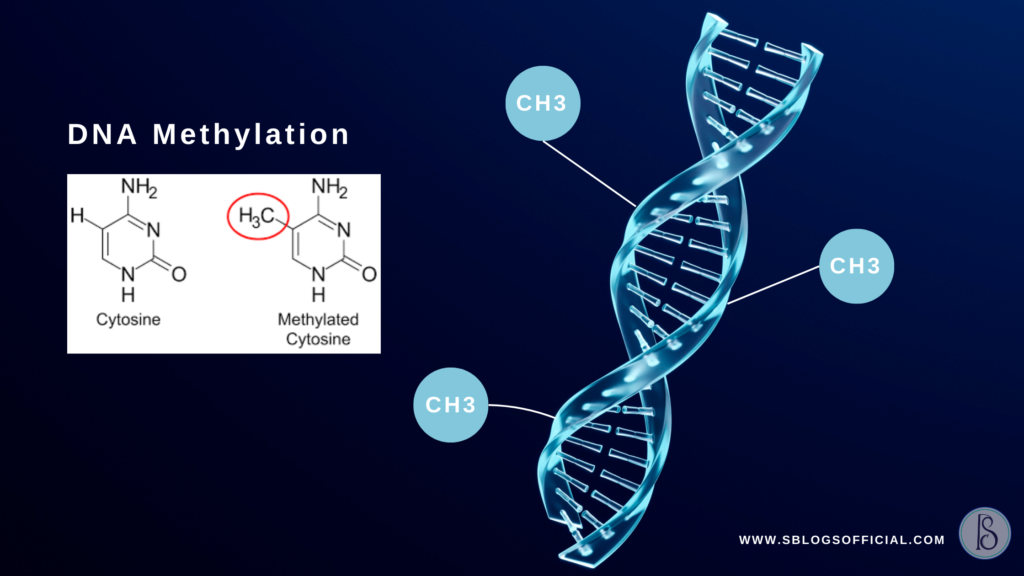
DNA Methylation is an epigenetic modification of high interest. It is your body’s Dimmer Switch that controls gene expression without changing the DNA. Where the small Chemical Methyl Group Attaches to DNA. It acts as a silencer, blocking the specific part of DNA by turning the gene on and off without altering the DNA sequence, typically at cytosine bases followed by Guanine (CpG sites). Methylation of CpG islands results in stable silencing of gene expression, and it is also associated with the control of gene expression.
Methylation plays a critical role in:
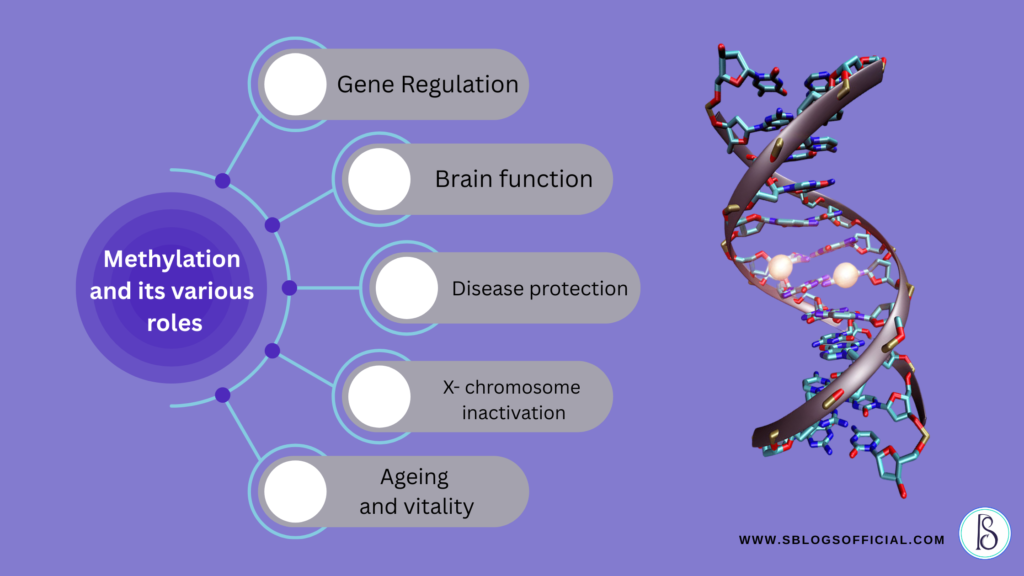
- Gene Regulation: Methylation helps in gene expression by activating or silencing genes at the appropriate time and specific cells. It helps in growth and development.
- Brain function: Methylation is essential for producing and breaking down key brain chemicals like serotonin, Dopamine, and Norepinephrine. For instance, if methylation is too slow, it will lead to anxiety, irritability, and agitation. If it’s too fast, it will cause depression, brain fog, and low motivation.
- Disease protection: Abnormal DNA methylation Patterns are associated with diseases like cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders. These patterns can be traced to early diagnosis and treatment.
- X- chromosome inactivation: In females, one of the two X chromosomes in each cell is turned off through methylation. This ensures that females, like males, have one functional X chromosome in each cell.
- Ageing and vitality: Aging is strongly correlated with changes in DNA methylation. DNA methylation and epigenetic alterations have been directly linked to longevity, aging, age-related disease, and rejuvenation in a wide array of organisms and humans.
What Is a Methylation Genetic Test?
Methylation gene test offers important information about the status of methylation in specific genetic variants in genes.
How it’s conducted: a saliva or blood sample
To conduct a genetic test on a patient, a DNA sample should be extracted from a saliva or blood sample. DNA extracted from saliva is a mixture of both bacterial and human DNA derived from epithelial and immune cells in the mouth.
Saliva sampling also has technical advantages over blood. It is non-invasive, does not require specialized equipment or training, and can be stored at room temperature for more than a year, making it feasible to sample outside of a laboratory.
Furthermore, the collected sample is sent to the laboratory for a methylation test. These tests measure the level of specific biomarkers associated with methylation, detecting abnormalities and providing insights into the regulation of gene expression and overall cellular health. Testing methylation includes analysis of specific common markers (MTHFR, COMT, MTRR, and more), which indicate the level of methylation in the body.
MTHFR gene Test:
The production of this MTHFR (Methylene tetrahydrofolate Reductase), an enzyme, is regulated by a gene. This enzyme, which is present in your body, is essential for the processing of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Having this mutation may lead to the accumulation of high levels of homocysteine in the blood and low levels of folate and other vitamins. Its crucial role is to direct the development of MTHFR proteins, which help the body to produce folate. This folate or folic acid is a type of vitamin B which is essential for creating DNA.
COMT:
Abbreviation COMT is Catechol-O-Methyl-Transferase is an enzyme responsible for the degradation of catecholamines. Such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These are important neurotransmitters that affect mood, emotions, and cognition. A deficiency of this enzyme may lead to a buildup of catecholamines in the body.
CBS:
Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency, also known as classical homocystinuria, is an autosomal metabolic disorder of sulfur metabolism due to a variation on cbs located on chromosome 21q33.3. It converts homocysteine into cystathionine, which is then converted into cysteine by the action of cystathionine-gamma-lyase.
Methylation DNA Test vs. Other Genetic Tests
Methylation is an epigenetic modification. The small Chemical Methyl Group (CH3) attaches to DNA, turning the gene on and off without altering the DNA sequence. It looks at whether the MTHFR gene is active or inactive. Mainly, it is affected by lifestyle, environment, diet, or even stress. Unlike methylation tests, genetic tests analyse the mutation or variants in the code, like a mutation in the BRCA1 gene, which is linked with breast cancer. Genetic tests might help you to figure out the MTHFR mutation; meanwhile, it identifies the MTHFR gene methylated without mutation. The methylation test reflects gene activity, which may vary with diet, stress, aging, and brain fog.
What Can a Methylation Gene Test Tell You?
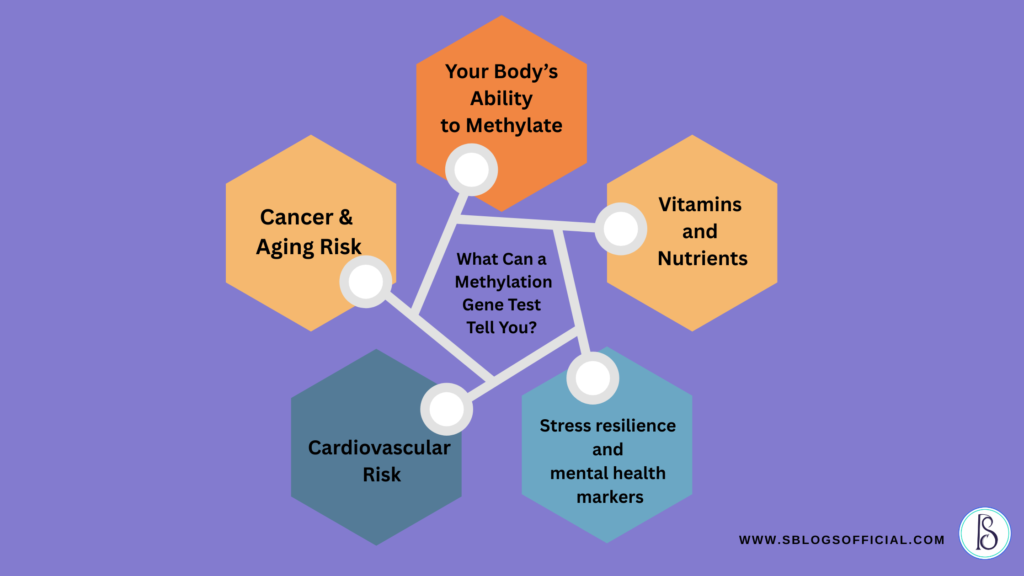
- Your Body’s Ability to Methylate
Methylation is your body’s Dimmer Switch that controls gene expression without changing the DNA. It checks for genes like MTHFR, COMT, MTRR & CBS Mutations.
- Vitamins and Nutrients
Treatment of MTHFR gene mutation is not required unless only if you have high Homocysteine levels. Eating folate-rich food may tend to help, or there are some folic acid supplements as well as Vitamin B6 and Vitamin B12.
- Stress resilience and mental health markers
COMT genes regulate neurotransmitters. The common symptoms of the COMT gene are depression, Anxiety, mood swings, insomnia, and headaches. Some variations may be associated with mental illness in people. Researchers have also linked potential connections between COMET with schizophrenia, bipolar disorders, panic disorder, anxiety, OCD, eating disorders, and ADHD.
- Cardiovascular Risk
MTHFR deficiencies may increase the risk of developing hyperhomocysteinemia, including Homocystinuria, or a mild form of hyperhomocysteinemia. This may further affect body function, such as cardiovascular risk, mood, detoxification, and fertility.
- Cancer & Aging Risk
Aging and cancer are associated processes at both the epidemiological and molecular levels.
Who Should Consider a Genetic Methylation Test?
- Family History of Long-Term Health Conditions like cancer, heart failure, autoimmune, and some mental health disorders.
- Often experiencing mood swings, persistent fatigue, anxiety, depression, and brain fog.
- Individuals with a high rise in homocysteine and cardiovascular risk.
- The history of cancer in family genetics methylation tests can come in handy.
- For a healthy lifestyle, individuals seek proper diet plans or supplements.
Limitations and Considerations of Methylation.
- It indicates that the inherited potential does not show the real-time results. Like the status of methylation at a moment.
- These tests cannot act as a diagnostic tool; there is a prompt need for a comparative study with medical history, and they cannot be fully relied upon.
- To start with supplements, one should always consider clinical advice from a genetic counsellor or clinical geneticist.
How to Start with Genetic Methylation Testing
To begin with the methylation testing, it’s important to first have a proper understanding of any existing chronic health conditions. There are many well-reputed genetic laboratories that offer these tests, but strongly recommended to consult your doctor before starting with supplements.
A non-invasive way of collecting your sample is saliva, which has traces of your DNA. Once your results are available, it is necessary to seek the professional opinion of a healthcare provider for accuracy. An overload of certain information can cause anxiety when you have no expertise in interpreting your test results. Routine monitoring of your B12, folate is a must, which is typically assessed by performing blood tests, for optimal function of methylation.
Final Thoughts: Your Blueprint Is the Beginning, Not the End
Genetics play vital roles in shaping our overall health system, mainly when it comes to chronic diseases that we experience. Genetic methylation tests provide you with insights into your blueprint, although it‘s just the starting point. To work beyond your genetic blueprint, it is essential to have control over lifestyle, nutrition, mindfulness, and surroundings. Physical activity is a must to strengthen your cardiovascular system. These tests give you insights into the potential of your body that don’t define you. What defines you is your way of taking into consideration your habits, professional care, and routine monitoring.
References:
- Johnson AA, Akman K, Calimport SR, Wuttke D, Stolzing A, de Magalhães JP. The role of DNA methylation in aging, rejuvenation, and age-related disease. Rejuvenation Res. 2012 Oct;15(5):483-94. doi: 10.1089/rej.2012.1324. PMID: 23098078; PMCID: PMC3482848.
- Sant KE, Nahar MS, Dolinoy DC. DNA methylation screening and analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;889:385-406. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-867-2_24. PMID: 22669678; PMCID: PMC3592359.
- Nishitani S, Parets SE, Haas BW, Smith AK. DNA methylation analysis from saliva samples for epidemiological studies. Epigenetics. 2018;13(4):352-362. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2018.1461295. Epub 2018 Aug 1. PMID: 29912612; PMCID: PMC6140812.
- Aging and cancer epigenetics: Where do the paths fork? – Pérez – 2022 – Aging Cell – Wiley Online Library
- Behind the Scenes of Gene Expression | Science
- Moore, L., Le, T. & Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacol 38, 23–38 (2013).
- Candela, E.; Zagariello, M.; Di Natale, V.; Ortolano, R.; Righetti, F.; Assirelli, V.; Biasucci, G.; Cassio, A.; Pession, A.; Baronio, F. Cystathionine Beta-Synthase Deficiency: Three Consecutive Cases Detected in 40 Days by Newborn Screening in Emilia Romagna (Italy) and a Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Children 2023, 10, 396.
