Imagine if your body could grow back damaged parts just like a lizard regrowing its tail. Sounds like science fiction, doesn’t it? Well, cell therapy (stem cell) is making this dream closer to reality than you might think. These remarkable treatments use our body’s own repair system – stem cells – to fix everything from damaged hearts to worn-out joints. Think of stem cells as your body’s ultimate handymen: they’re incredibly versatile cells that can transform into almost any type of tissue your body needs. Whether it’s brain cells to treat Parkinson’s disease, heart muscle to repair damage after a heart attack, or cartilage to ease arthritis pain, stem cells offers hope where traditional medicine often falls short.
The UK is at the forefront of this medical revolution, with success rates of 60-70% for certain blood cancers using stem cell transplants, and survival rates reaching 79% three years post-treatment for hematopoietic stem cell transplants. From treating diabetes with reprogrammed cells to helping paralysed patients regain movement, stem cell therapy isn’t just changing individual lives – it’s revolutionising how we think about healing itself. The market is booming too, with global stem cell therapy expected to grow from $16.4 billion in 2024 to $37.7 billion by 2033, proving that this isn’t just medical hype – it’s the future of healthcare.
1. What Exactly Are Stem Cells and How Do They Work?
Cell therapy (stem cell) relies on understanding what makes these cellular superstars so special and powerful.
- Stem cells are “blank slate” cells that can develop into many different cell types
- They can divide and create copies of themselves indefinitely
- They naturally repair damaged tissues throughout your body
- There are different types: embryonic, adult, and induced pluripotent stem cells
- Adult stem cells are found in bone marrow, fat, blood, and other tissues
- They respond to chemical signals telling them what type of cell to become
Cell therapy works by harnessing these natural repair mechanisms and supercharging them. Think of your body as a construction site that’s constantly under repair. Stem cells are like skilled workers who can learn any trade – they might become carpenters (bone cells), electricians (nerve cells), or plumbers (blood vessel cells) depending on what your body needs. When you’re injured or ill, your body sends out distress signals, and stem cells rush to the scene. However, sometimes there aren’t enough of them, or they can’t get to the right place. That’s where cell therapy steps in, providing extra workers or directing them exactly where they need to go. Scientists can now grow millions of these cells in laboratories and even reprogram regular cells to behave like stem cells, opening up incredible possibilities for treatment.
Also read- Genetic Methylation Testing: Unlocking Your Body’s Cellular Programming Secrets
2. Types of Stem Cell Therapy Treatments Available Today
Modern medicine offers several different approaches to cell therapy, each suited to different conditions and needs.
- Bone marrow transplants for blood cancers and immune system disorders
- Adipose (fat) stem cell therapy for joint problems and tissue repair
- Cord blood stem cell treatments for genetic and immune conditions
- Induced pluripotent stem cell therapy for various degenerative diseases
- Mesenchymal stem cell injections for arthritis and sports injuries
- Neural stem cell therapy for brain and spinal cord conditions
The variety of stem cell treatments reflects how versatile these cells truly are. Bone marrow transplants, the oldest form of stem cell therapy, have been saving lives for over 50 years. Bone marrow transplants show a 92% survival rate at three-year follow-up, making them one of the most successful cancer treatments available. More recent developments include using stem cells from your own fat to treat arthritis – a much less invasive option than major surgery. Cord blood therapy uses stem cells collected from umbilical cords, which are incredibly potent and less likely to be rejected by the immune system. Scientists have also developed ways to take regular skin cells and reprogram them back into stem cells, called induced pluripotent stem cells. This breakthrough means we can potentially create personalised treatments using a patient’s own cells, eliminating the risk of rejection.
3. Conditions Successfully Treated with Cell Therapy (Stem Cell)
Cell therapy has shown remarkable success across a surprisingly wide range of medical conditions and diseases.
- Blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphoma with high success rates
- Heart disease and damage from heart attacks
- Diabetes through beta cell replacement therapy
- Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions
- Spinal cord injuries and paralysis
- Osteoarthritis and joint degeneration
- Multiple sclerosis and autoimmune disorders
- Burns and severe skin damage
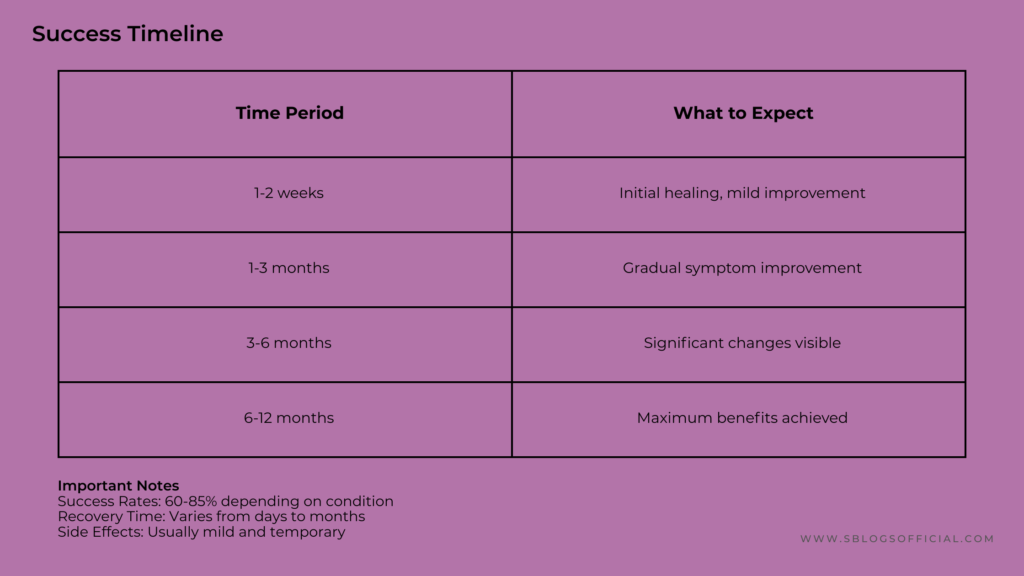
The success stories of cell therapy read like medical miracles, but they’re backed by solid science. Blood disorder treatments show a 72% survival rate after three years, whilst recent breakthroughs include researchers injecting 1.5 million reprogrammed stem cells to treat diabetes. Heart patients are seeing remarkable improvements when stem cells are injected directly into damaged heart muscle, helping to regrow healthy tissue and improve pump function. For Parkinson’s patients, stem cells can potentially replace the brain cells that produce dopamine, offering hope for millions worldwide. Perhaps most exciting are the early trials for spinal cord injuries, where patients with complete paralysis have regained some movement and sensation. Arthritis sufferers are finding relief through stem cell injections that help rebuild cartilage naturally, avoiding the need for joint replacement surgery.
Also Read- What Is a DNA Antibody Blood Test: A Window into Your Immune System?
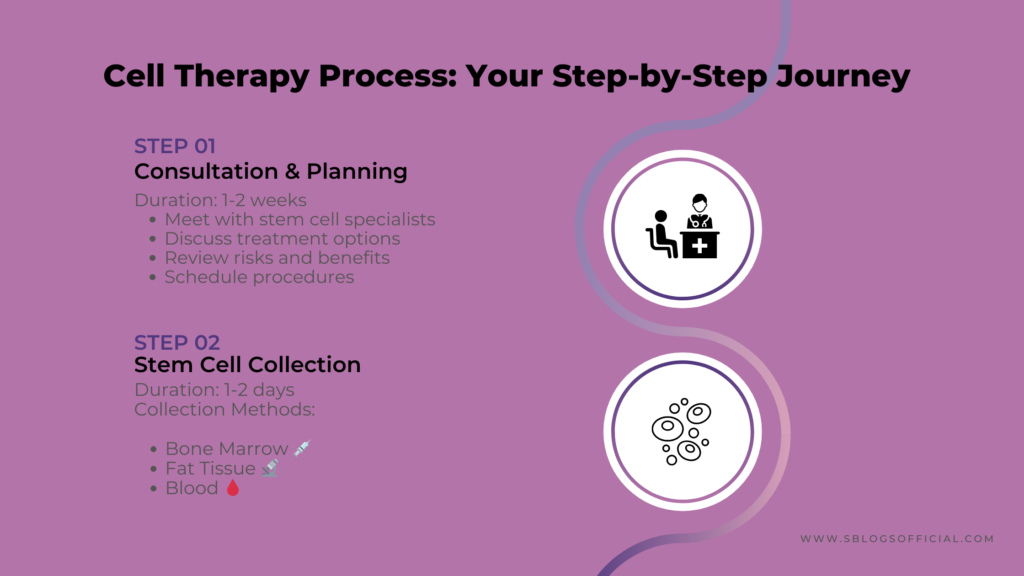
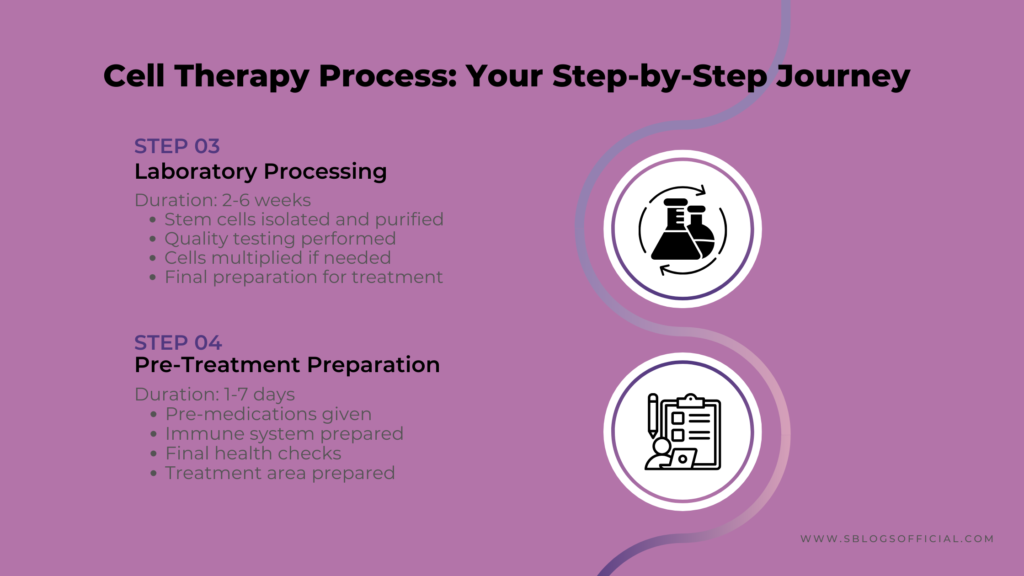
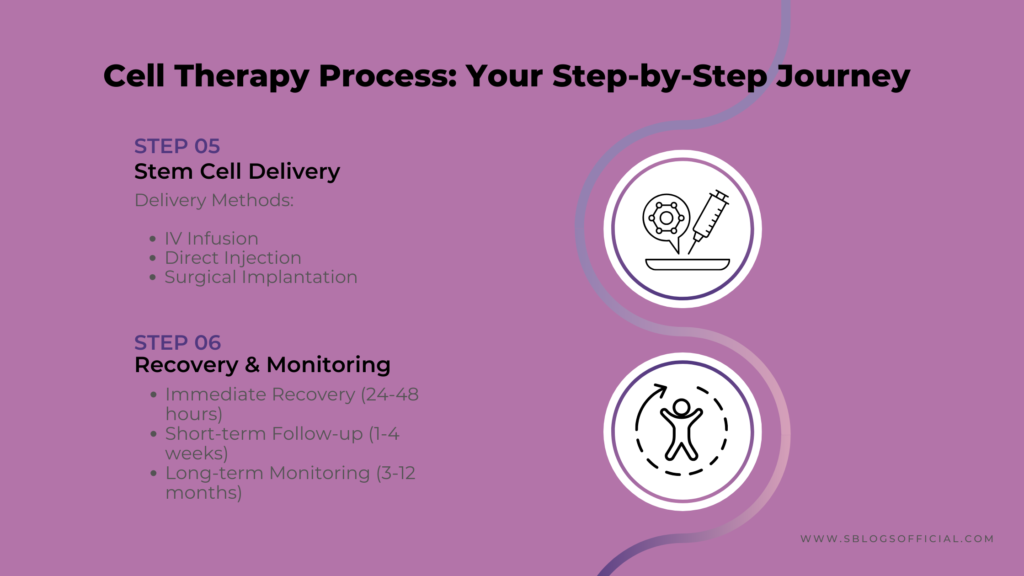
4. The Cell Therapy (Stem Cell) Process: What to Expect
Understanding what happens during cell therapy treatment helps patients prepare and know what to expect.
- Initial consultation and medical evaluation with specialists
- Stem cell collection through bone marrow aspiration or fat removal
- Laboratory processing and cell multiplication over several weeks
- Pre-treatment preparation including possible chemotherapy
- Stem cell infusion or injection at the treatment site
- Recovery period with careful monitoring for complications
- Follow-up appointments to track progress and effectiveness
The stem cell process varies depending on your specific treatment, but most follow a similar pattern. For bone marrow treatments, you’ll first undergo tests to ensure you’re healthy enough for the procedure. The actual stem cell collection might feel uncomfortable but isn’t usually painful – it’s similar to giving blood but takes longer. If you’re having your own stem cells used, they’ll be processed and sometimes grown in the lab to increase their numbers. The actual treatment day is often surprisingly straightforward – stem cells are typically given through an IV drip, much like a blood transfusion. Recovery varies enormously depending on the condition being treated. Some patients feel improvement within weeks, whilst others may need several months to see results. The monitoring period is crucial because doctors need to ensure the stem cells are working properly and not causing any unwanted side effects.
5. Costs and Availability of Stem Cell Therapy in the UK
Stem cell therapy costs vary significantly depending on the treatment type and complexity of the condition being addressed.
- Basic treatments range from £3,500 to £25,000 depending on complexity
- Advanced treatments can cost up to £100,000 for complex conditions
- NHS covers established treatments like bone marrow transplants
- Private treatment required for many experimental or newer therapies
- Some treatments available through clinical trials at no cost
- Travel abroad sometimes necessary for certain experimental treatments
Stem cell therapy in the UK costs between £3,500 and £25,000, depending on the treatment type, with some complex treatments reaching £100,000. The NHS provides excellent coverage for established stem cell therapy treatments, particularly bone marrow transplants for cancer patients. However, newer or experimental treatments often require private payment or participation in clinical trials. NHS Blood and Transplant has developed a ten-year vision for stem cell transplantation that focuses on creating a high-quality and sustainable service, which should improve access over time.
Many patients find that participating in clinical trials offers access to cutting-edge treatments at no cost, though this requires meeting strict eligibility criteria. The UK stem cell therapy market is expected to grow from £1.02 billion in 2024 to £3.1 billion by 2035, suggesting that costs may decrease as treatments become more mainstream and competition increases.
Also Read- Can You Get More Than One Autoimmune Disease? Understanding the Complex World of Immune System Challenges
6. Future of Cell Therapy (Stem Cell): What’s Coming Next?
The future of cell therapy (stem cell) holds incredible promise with new developments emerging regularly in research laboratories worldwide.
- Personalised stem cell treatments tailored to individual genetic profiles
- 3D bioprinting of organs using patient’s own stem cells
- Gene editing combined with stem cell therapy for genetic diseases
- Off-the-shelf stem cell products that don’t require immune matching
- Stem cell therapy for ageing and longevity enhancement
- Integration with artificial intelligence for treatment optimisation
- Combination therapies using stem cells with other advanced treatments
The future of stem cell therapy is incredibly exciting, with developments that sound like science fiction becoming reality. Scientists are working on growing entire organs in laboratories using stem cells – imagine replacing a damaged heart with one grown from your own cells! Gene editing technologies like CRISPR are being combined with stem cell therapy to correct genetic defects before the cells are transplanted back into patients. Researchers are also developing “universal” stem cells that could work in any patient, eliminating the need for matching and making treatments much more accessible. Perhaps most intriguingly, some scientists believe cell therapy could help us live longer, healthier lives by replacing worn-out cells throughout our bodies. The combination of artificial intelligence with stem cell research is accelerating discoveries, helping scientists predict which treatments will work best for specific patients.
Cell Therapy (Stem Cell): Hope for Tomorrow’s Medicine
Cell therapy (stem cell) represents one of the most promising frontiers in modern medicine, offering hope to millions of patients with conditions that were previously considered untreatable. From the remarkable success rates in blood cancers to breakthrough treatments for diabetes and heart disease, these therapies are already changing lives across the UK and beyond. While costs remain high for many experimental treatments, the growing market and increasing NHS investment suggest that stem cell will become more accessible over time. As we look to the future, the combination of stem cells with gene editing, 3D printing, and artificial intelligence promises even more revolutionary treatments. For patients and families affected by serious illness, stem cell therapy offers something invaluable: genuine hope backed by solid science.
For more information about stem cell treatments and clinical advantages, stay tuned with us we are having a series of posts related to cell therapy and stem cell therapy.
