
Hereditary disease screening is a medical test done to look at your DNA, which identifies any changes or mutations that may lead to inherited diseases passed down from your parents.
It is a type of health check initiative that is offered to certain groups of people who don’t have any symptoms. The idea is to spot those who might be at higher risk for inherited conditions, so they can take steps early, like getting preventive care, starting treatments sooner or making informed choices about having their children. Genetic material carries a lot of information which is essential for the determination of individual traits such as eye colour, skin tone, which are inherited by a child from their parents.
Must-Know Terms in Genetic Screening for Hereditary Disease Screening
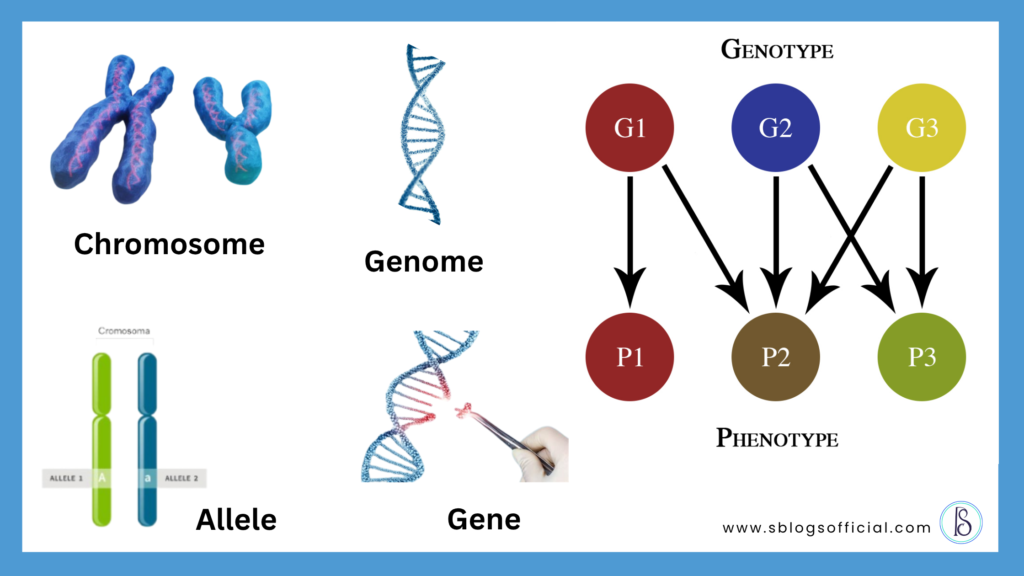
Gene: Imagine having a blueprint of your body’s health responses — your genes. In simple terms, if we describe DNA, it acts like a Recipe Book for your body; meanwhile, genes are the recipes inside of your DNA that instruct your body how to make certain proteins. basically, they both act as an instruction manual which teaches your body how to function.
Chromosome: it is like a tiny molecular package that carries your DNA in the nucleus of a cell, which instructs your body how to function and develop
Genome: the entire genetic material includes all chromosomal sets of living beings.
Allele: multiple versions of the same gene
Genotype: it is your unique set of genes that give rise to an individual’s phenotype
Phenotype: how your genes show up physically, your outer appearance
What diseases can be detected through genetic testing?
In Hereditary disease screening, Genetic Carrier Screening is a type of genetic test which analyses whether the particular individual is a carrier of genes for a specific disorder. Carrier screening is used to identify couples who are at higher risk of having offspring with an autosomal recessive disorder. For a disorder to occur, a person must inherit one defective gene from the mother and one from the father. If an individual receives the defective gene from only one parent, they are considered carriers.
In most cases, carriers do not exhibit any symptoms, although mild signs may occasionally appear. This test is typically performed before or during pregnancy, which helps to identify the risk of genetic disorders in the child. A carrier screening test or hereditary disease screening is mostly done by requiring a sample of a person’s blood, saliva or tissue. When a particular person is found to be a carrier of a specific condition, that person is tested first; if found negative, no further test is required. However, if it is found to be positive, then the other partner is also tested, and further, they are counselled.
Also Read- Genetic Methylation Testing: Unlocking Your Body’s Cellular Programming Secrets
Carrier Screening Purpose:
- Identifies changes in genes linked to disorders and diseases
- Focuses on common genetic conditions with a higher risk in certain population groups that can be detected via hereditary disease screening
Common Genetic Conditions Included in Carrier of Hereditary Diseases Screening:
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- Affects motor neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem
Cystic Fibrosis
- Mainly affects the lungs and digestive system
Hemoglobinopathies
- Affect the production of haemoglobin
Fragile X Syndrome
- One of the most common causes of learning disabilities
- Can sometimes cause behavioural problems
Thalassemia
- Blood disorder resulting in less haemoglobin than normal
Sickle Cell Disease
- Blood disorder where red blood cells become ‘C’ shaped
- Makes it difficult for blood to move smoothly through blood vessels
Interestingly, a lot of these genetic conditions tend to show up more often in specific communities or ethnic backgrounds such For Canavan disease is a severe degenerative neurologic disease. Familial dysautonomia, a disorder of the sensory and autonomic nervous system, Bloom syndrome is characterised by short stature, skin rash with sun exposure, and increased risk of cancer of any type. Usher syndrome is characterised by impairments in vision, balance, and hearing. Tay–Sachs disease is, progressive neurodegenerative disease.
Typically affects Eastern European and Central European Jewish descent, while the detection rate in non-Jewish individuals is unknown for most of these disorders, except for Tay–Sachs disease and cystic fibrosis. In Tay-Sachs disease, individuals of French–Canadian and Cajun descent also have a carrier frequency higher than that in the general population.
Also Read- Elderly Care Robots: How They Are Changing the Way of Care Giving
The Main Kinds of Genetic Testing You Should Know and What They Detect?
In hereditary disease screening, the main aim of genetic screening is to detect the higher risk of genetic abnormalities in an individual. Types of Genetic screening can be broadly divided into two categories: Diagnostic testing and screening, such as
Newborn screening:
The largest component of newborn hereditary disease screening involves obtaining a blood sample to screen for metabolic, hematologic, endocrine, and other inherited disorders. A sample of the infant’s blood is ideally obtained within 24-48 hours of birth, though premature or ill infants may require alterations to this screening timeline.
Carrier Screening:

Carrier screening is used to identify couples who are at higher risk of having offspring with an autosomal recessive disorder. For a disorder to occur, a person must inherit one defective gene from the mother and one from the father. If an individual receives the defective gene from only one parent, they are considered carriers.
(PGD) Preimplantation Genetic Diagnostics:
It is a test typically performed on embryos created through IVF (In Vitro Fertilisation). The purpose of PGD under hereditary disease screening is to screen embryos before transfer into the uterus, helping to detect genetic abnormalities, particularly aneuploidies (an abnormal number of chromosomes). There are 3 main types of PGD test: PGT-A, which detects an abnormal number of chromosomes; PGT-M, which detects single gene disorders that are carried by both parents, like cystic fibrosis; PGT-SR, which detects structural abnormalities in embryos.
Ultrasonography:
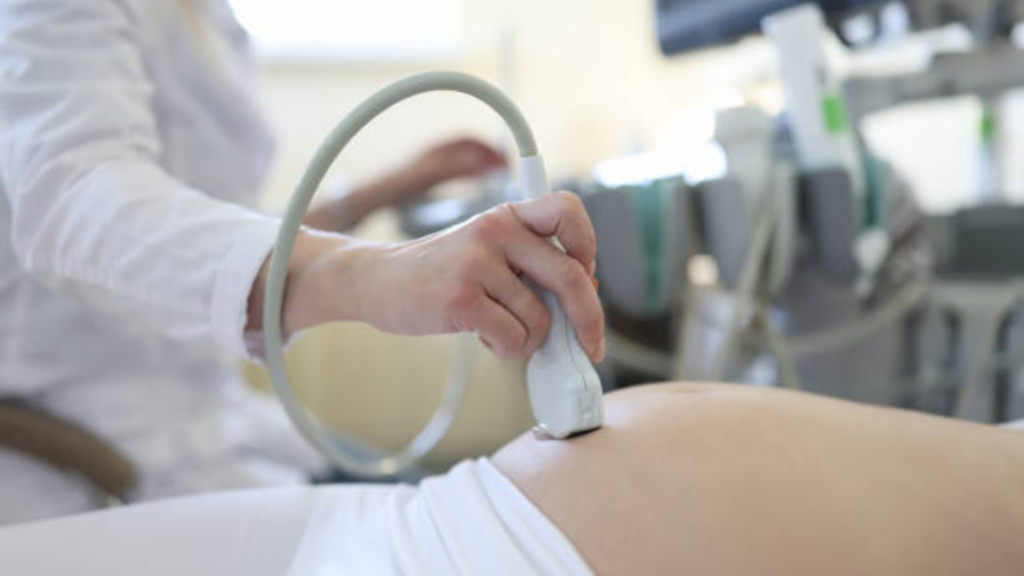
A transducer is placed above the mother’s abdomen to check for the growth of the foetus, which determines the size and position of the foetus. First to be visualised at 6 weeks of gestation, but for screening major internal abnormalities to be accomplished between 16-20 weeks of gestation. Ultrasonography mainly screens for structural abnormalities like Down syndrome.
Amniocentesis:
It is an invasive procedure of hereditary disease screening which determines the diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and other fatal problems like Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13), and Edward syndrome (Trisomy 18). Amniocentesis is mostly performed between 14-20 weeks of gestation.
Chorionic villi sampling:

an invasive procedure where a catheter is passed via the vagina into the cervix, allowing sampling of cells from the placental chorionic villi. CVS is mainly done for chromosomal analysis, which determines the karyotype of the foetus. CVS is performed mostly between 9-12 weeks of gestation.
Fatal Nuchal Translucency:
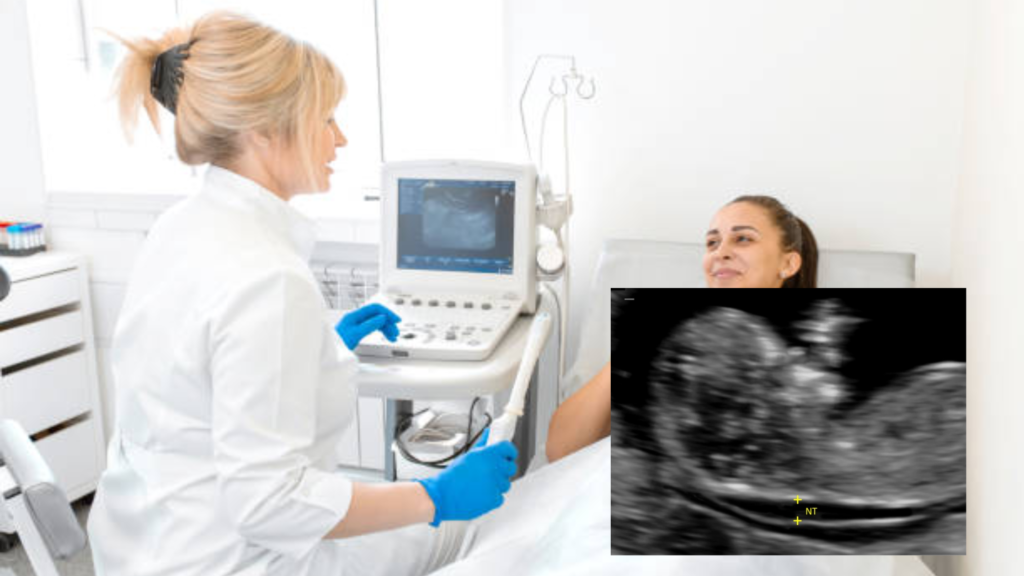
An Ultrasound scan that helps to assess the amount of fluid behind the neck of the foetus (known as the nuchal fold). The more fluid, the higher the risk of chromosomal abnormalities. Blood serum test for hereditary disease screening is performed to determine the level of two hormones, PAP-A and BETA HC. A combination of ultrasound and blood test helps to identify a higher risk of Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, Patau syndrome and Turner syndrome (45x).
Newborn screening:

blood screening is performed shortly after birth to detect genetic illnesses which have no visible effect.
Also Read- Amazing Facts About DNA: The Incredible Secrets Inside You
To Conclude, What Are the Key Facts Everyone Should Know About Genetic Screening?
Nowadays, Hereditary disease screening through genetic screening has become a mainstream method to detect carriers screening often in clinical practice and can be done by various techniques which assess the risk of recessive disorders. It mainly focuses on detecting and eliminating the transmission of diseases and boosting family planning without the burden of genetic illnesses.
Reference-
- Talking Glossary of Genetic Terms | NHGRI
- Andermann, A., & Blancquaert, I. (2010). Genetic screening: A primer for primary care. Canadian Family Physician Medecin de famille canadien, 56(4): 333–339.
- Carrier Screening for Genetic Conditions | ACOG
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. (2020). Prenatal genetic screening tests. In ACOG. Retrieved December 12, 2020, from
